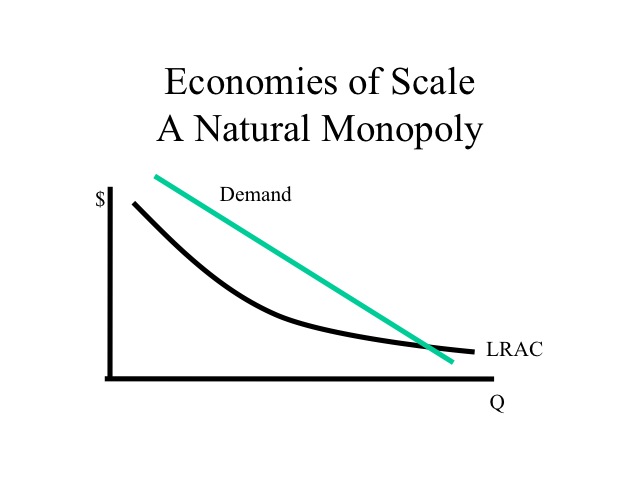
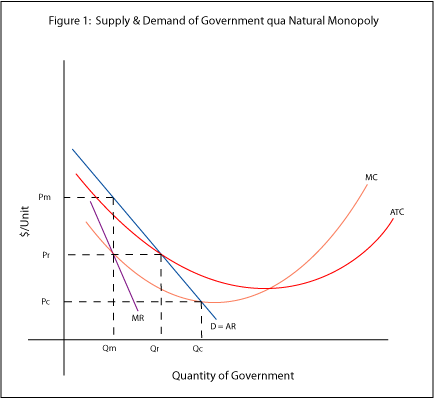
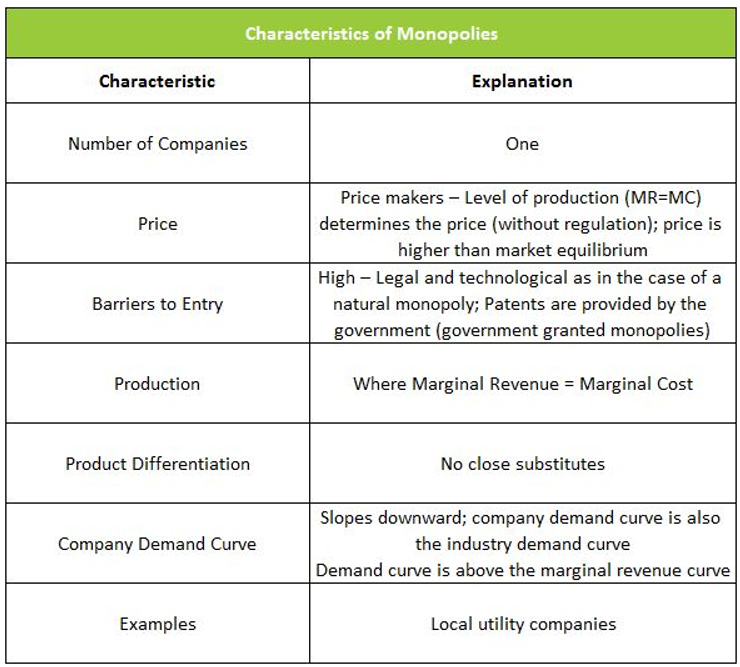
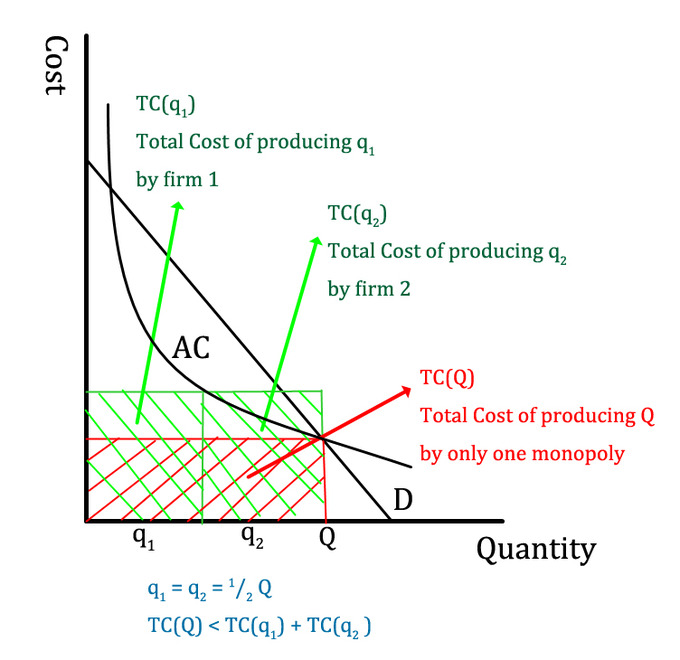
If the government regulates a natural monopolist to produce the allocatively efficient level of output, it will require the monopolist to set a price that is: a. equal to its marginal cost
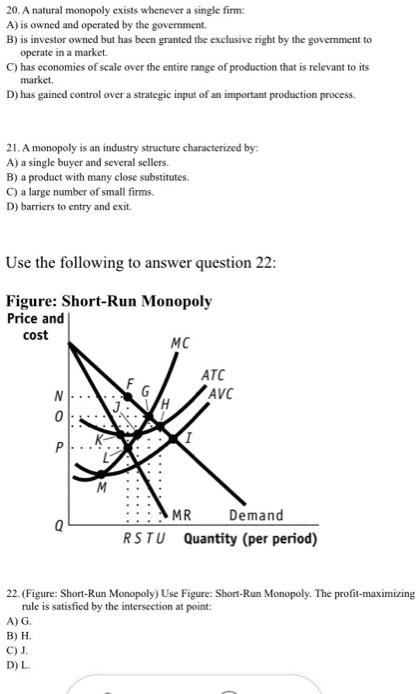
SOLVED: 20. A natural monopoly exists whenever a single firm: A) is owned and operated by the government. B) is investor owned but has been granted the exclusive right by the government

natural monopolies are impossible in a free market" - an "esteemed" professor and a "scholar" : r/EnoughLibertarianSpam

Monopoly. Monopoly A monopoly is one business firm that produces the entire market supply of a particular good or service. A monopoly is one business. - ppt download




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/natural_monopoly.asp-FINAL-6752adca612b4c648c1447518584dcd7.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/history-gender-wage-gap-america-5074898_sketch-455ef27d4b304765ba4830023fed50bb.jpg)